Conformity Certifications
MFDS
Republic of Korea
FDA
United States of America
PMDA
Japan
TFDA
Taiwan
CE
Europe
TGA
Australia
HSA
Singapore
ANVISA
Brazil
HC
Canada
01
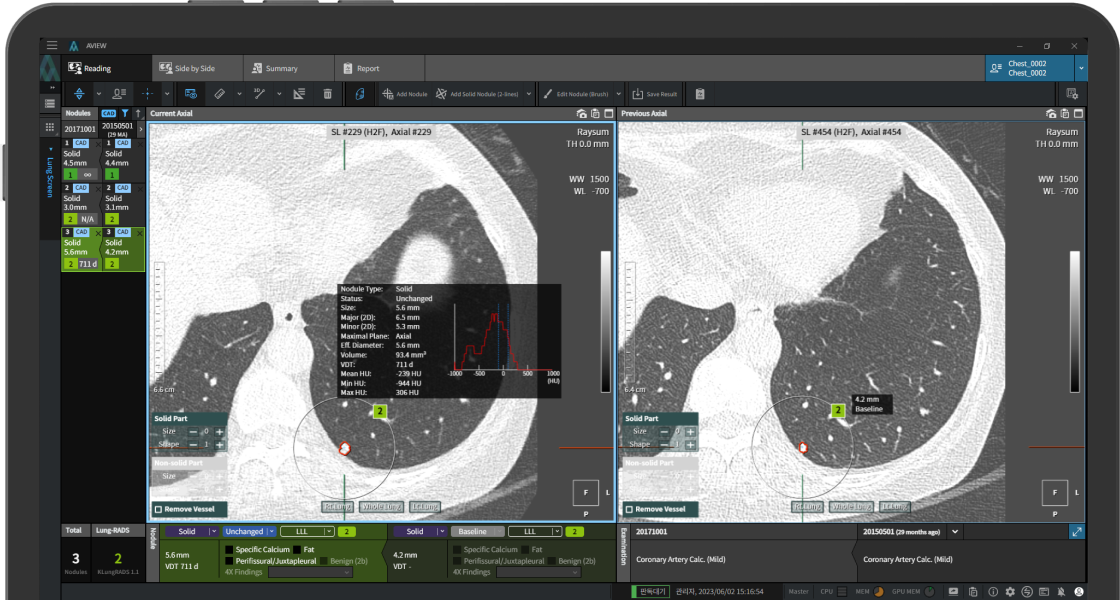
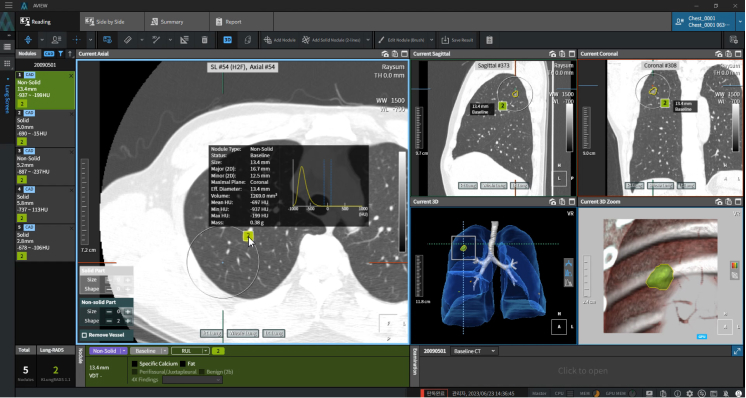
Detecting Nodules of Various Sizes, from Small to Large
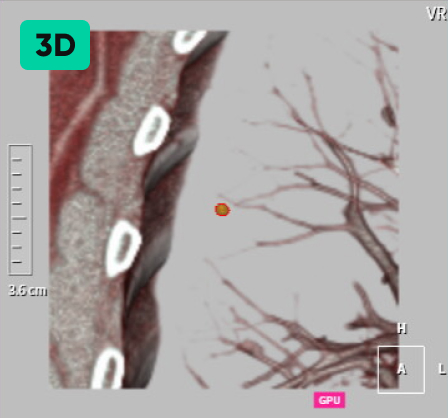
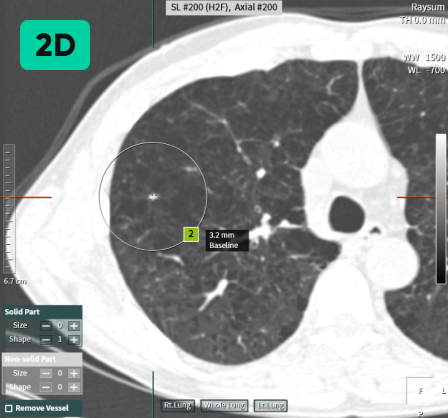
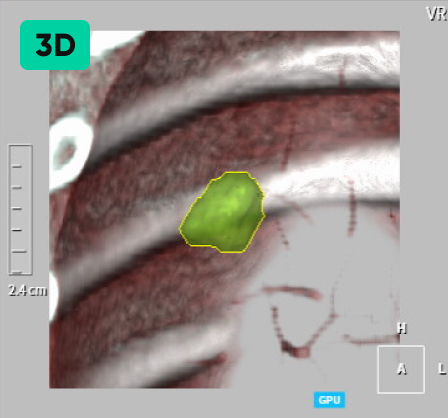
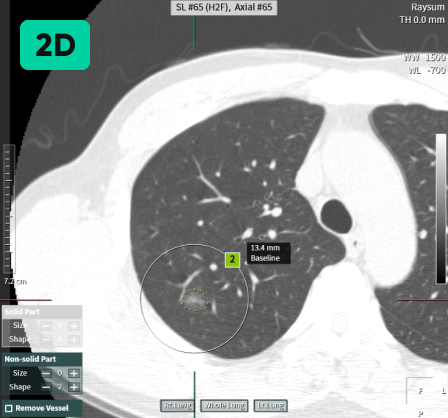
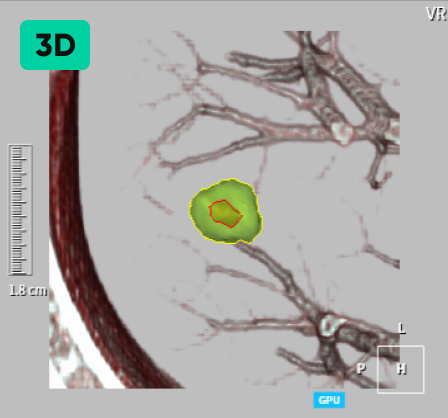
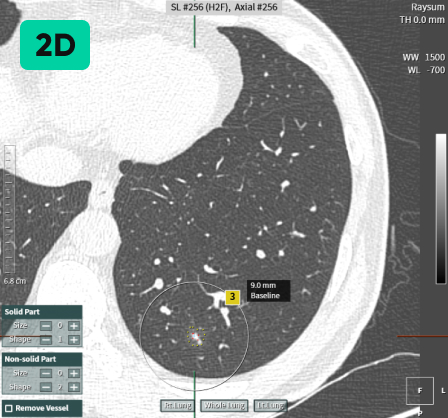
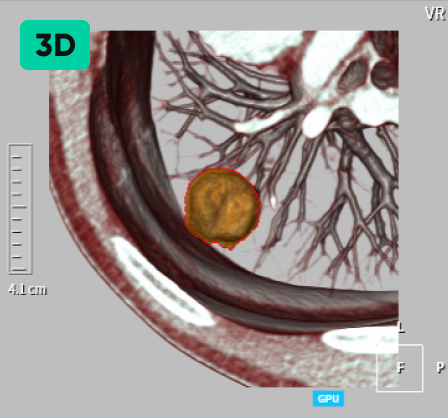
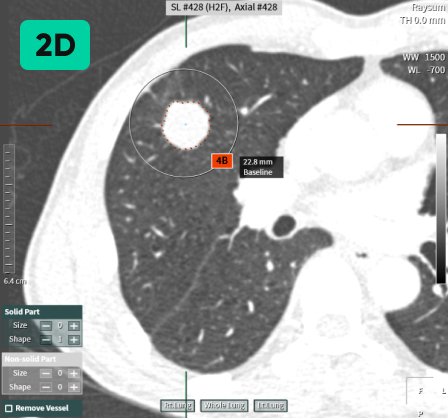
02
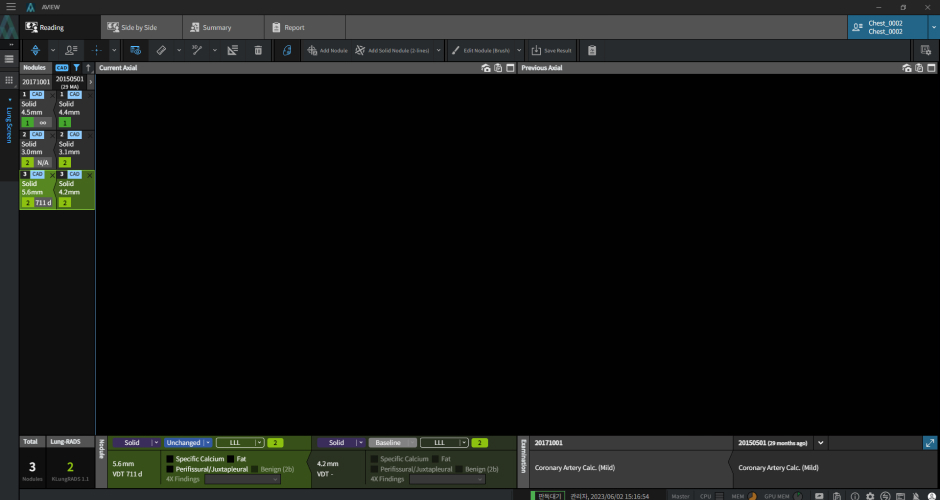
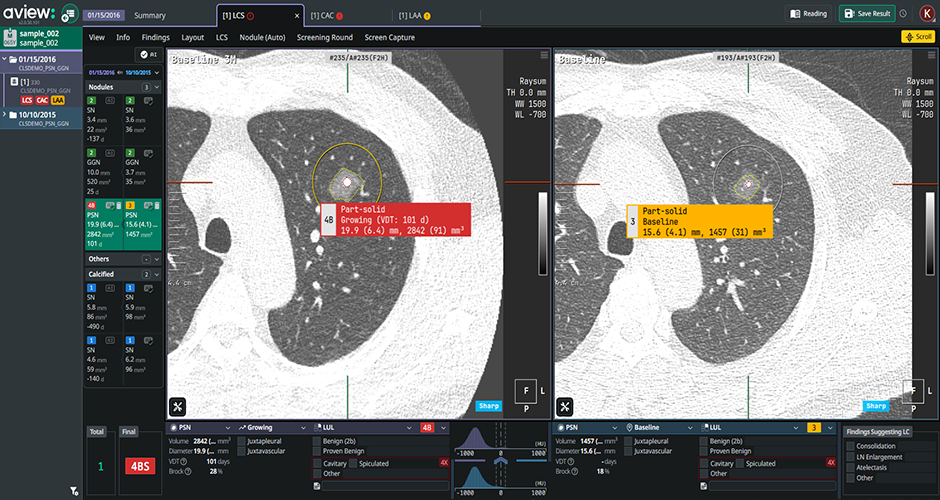
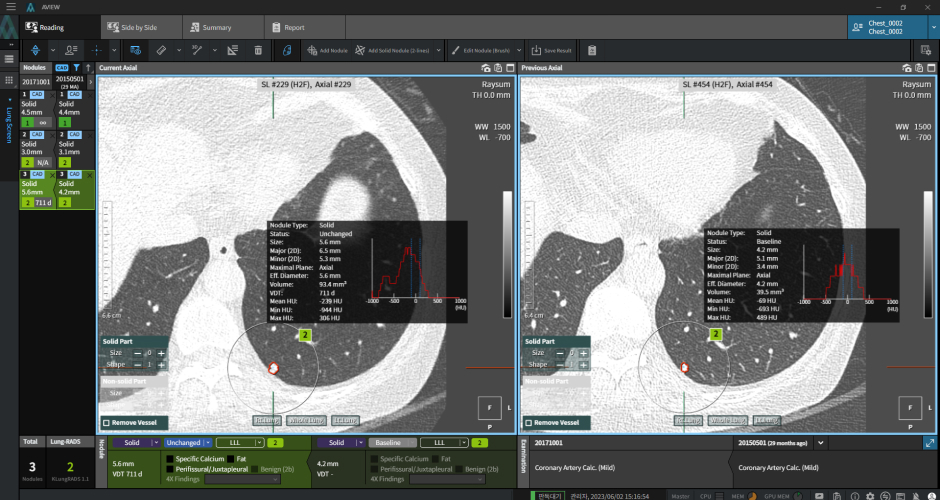
Follow-up CT Scan
Previous CT Scan

03

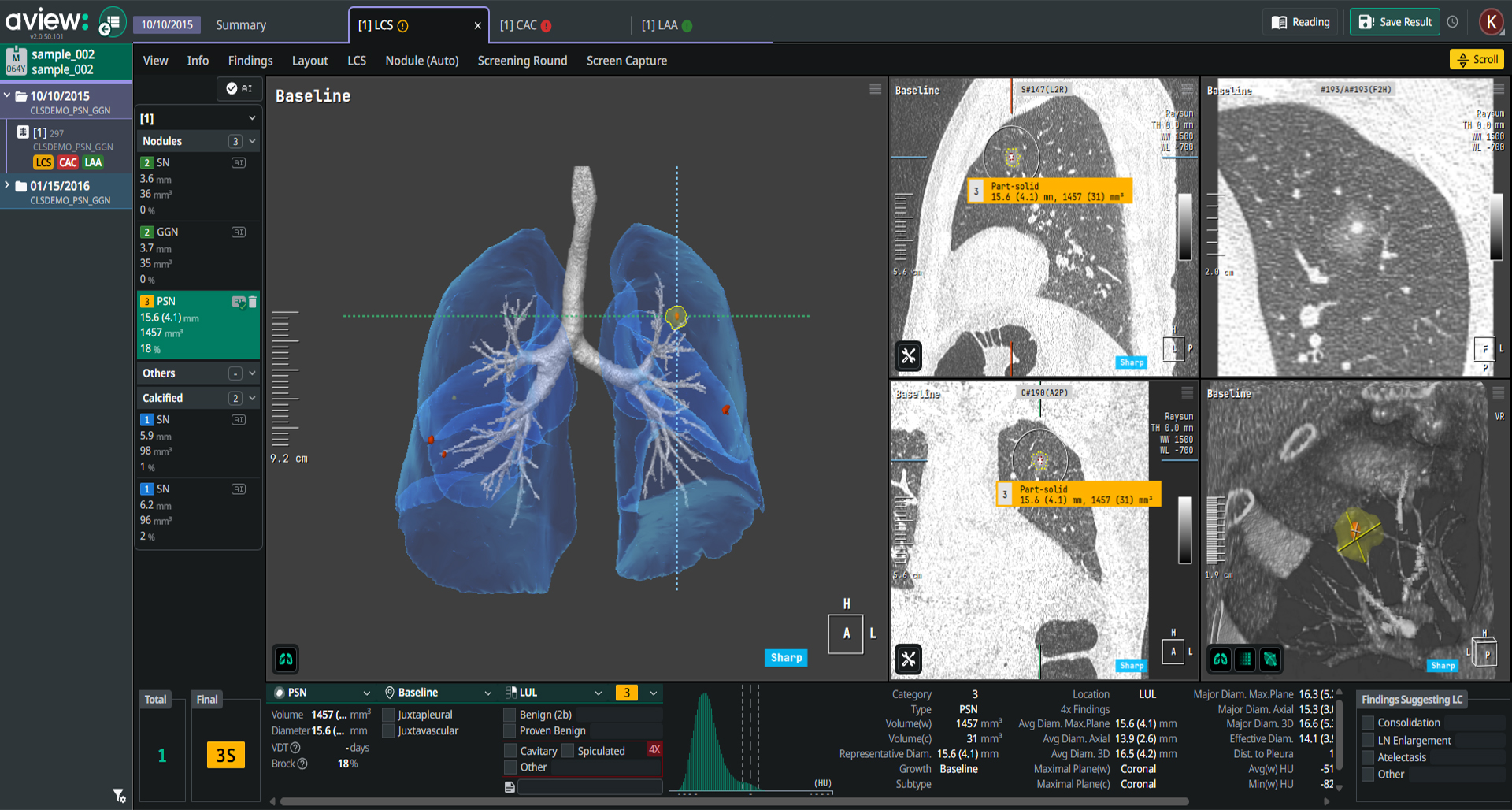
04
Reading report
Effortless Generation of Lung Cancer Screening Results for Patient Records and Official Reports.
Patient Reports and insurance reimbursement reports
Automatically generated reports with detail assist patients understand examination results.
Validations
Clinically Proven: AI Medical Technology Saves
Time and Enhances Reading Accuracy.
0
Time Saving
0
Sensitivity
23
false positivity rate
Reduce Workload

https://dailybulletin.rsna.org/db22/index.cfm?pg=22fri07

Lancaster HL, Zheng S, Aleshina OO, Yu D, Yu Chernina V, Heuvelmans MA, de Bock GH, Dorrius MD, Willem Gratama J, Morozov SP, Gombolevskiy VA, Silva M, Yi J, Oudkerk M. Outstanding negative prediction performance of solid pulmonary nodule volume AI for ultra-LDCT baseline lung cancer screening risk stratification. Lung Cancer. 2022 Jan 6;165:133-140
Publications
Refer to the following research papers
These contents represent summaries of scientific
publications and are unrelated to any form of advertising.

To evaluate performance of AI as a standalone reader in ultra-low-dose CT lung cancer baseline screening, and compare it to that of experienced radiologists. Volumetric nodule measurements were performed by five experienced blinded radiologists, and independently assessed using an AI lung cancer screening prototype (aview LCS, v1.0.34, Coreline Soft, Co. ltd, Seoul, Korea) to automatically detect, measure, and classify solid nodules. Our results suggest that through the use of AI as an impartial reader in baseline lung cancer screening, negative-misclassification results could exceed that of four out of five experienced radiologists, and radiologists’ workload could be drastically diminished by up to 86.7%.
Harriet L. Lancaster, Sunyi Zheng, et al. “Outstanding negative prediction performance of solid pulmonary nodule volume AI for ultra-LDCT baseline lung cancer screening risk stratification.” Lung Cancer


The Korean Lung Cancer Screening Project (K-LUCAS) is a single-arm cohort study that was conducted from February 2017 to evaluate the feasibility of implementing an organized national lung cancer screening program in Korea High-risk population aged 55–74 years with more than a 30-pack-year smoking history was recruited. The screening results were reported using the Lung Imaging Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS), suggested by the American College of Radiology. K-LUCAS was performed by a network-based diagnosis supporting system using a computer-aided detection (CAD) program (aview LCS, Corelinesoft) to maintain screening quality. K-LUCAS provided promising evidence supporting the implementation of a national lung cancer screening program to detect lung cancer at an early stage and promote smoking cessation for participants in Asian population.
Lee J, Kim Y, Kim HY, et al. “Feasibility of implementing a national lung cancer screening program: Interim results from the Korean Lung Cancer Screening Project (K-LUCAS). Transl Lung Cancer Res.” 2021;10(2):723-736.
